- HPLC Columns
- Close Menu ×
- C18 Columns
- Core-shell Columns
- C8 & C4 HPLC Columns
- HILIC HPLC Columns
- PFP & Phenyl HPLC Columns
- Bioseparation LC columns
- SEC HPLC Columns
- All HPLC Columns
- InertSustain C18 First choice for ultra-high inertness and high durability, delivering superior peak shapes with low back pressure.
- Inertsil ODS-3 Most popular C18, trusted for long-established methods, offering strong retentivity and high loading capacity.
- InertSustain AQ-C18 First choice for high-polarity compounds, delivering strong retention even under 100% aqueous mobile phases.
- Inertsil ODS-3V Validated version of ODS-3, designed for GLP/GMP compliance, ensuring batch-to-batch consistency.
- InertSustainSwift C18 Ultra-inert, fast-separation C18 for high-throughput LC-MS and LC-MS/MS with superior peak symmetry.
- InertSustain AX-C18 Mixed-mode C18 with anion exchange for strong retention of highly polar acidic compounds without ion-pairing.
- All C18 Columns visible-xs
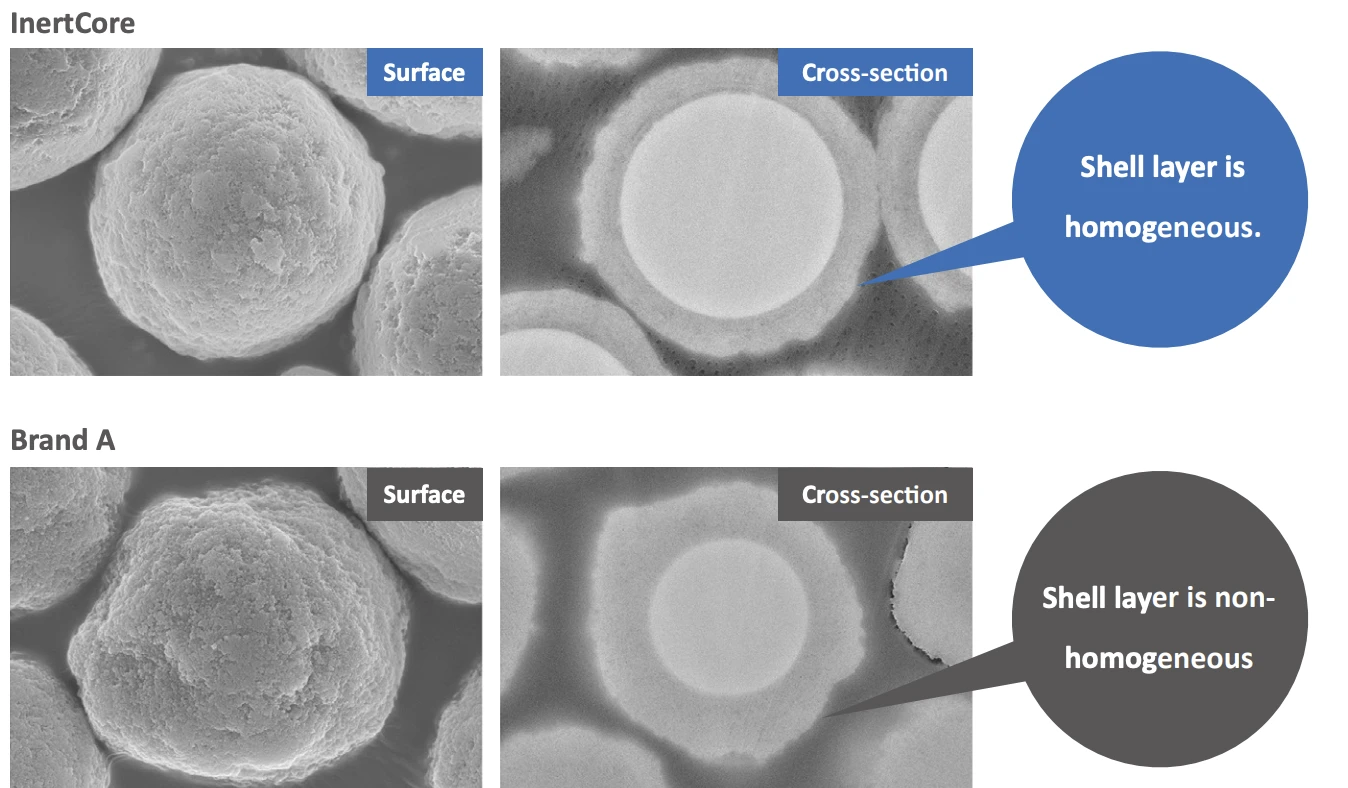
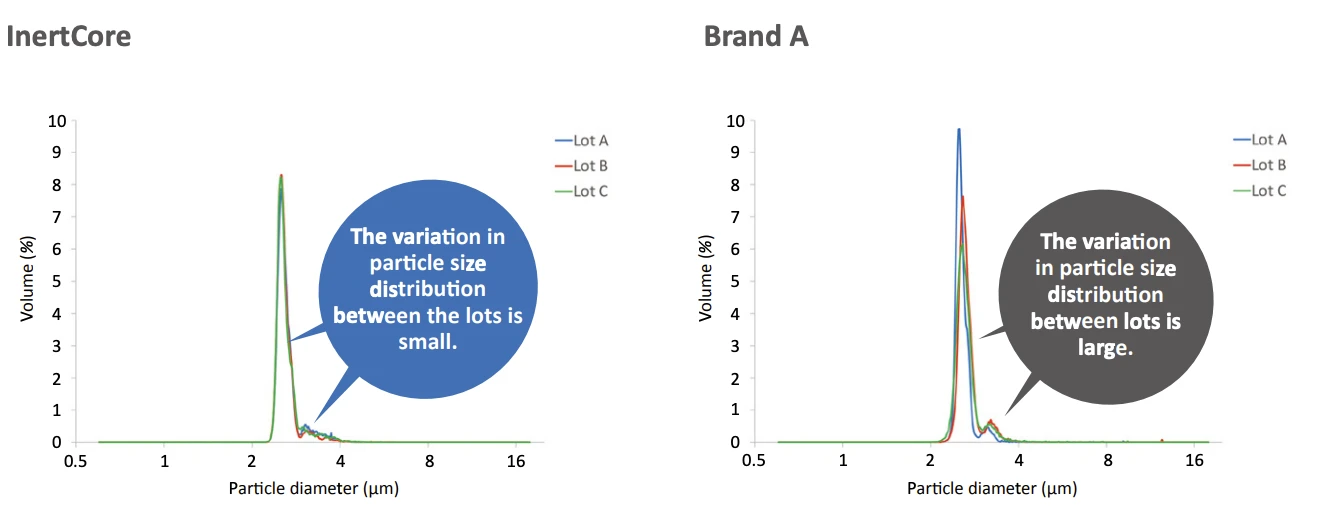
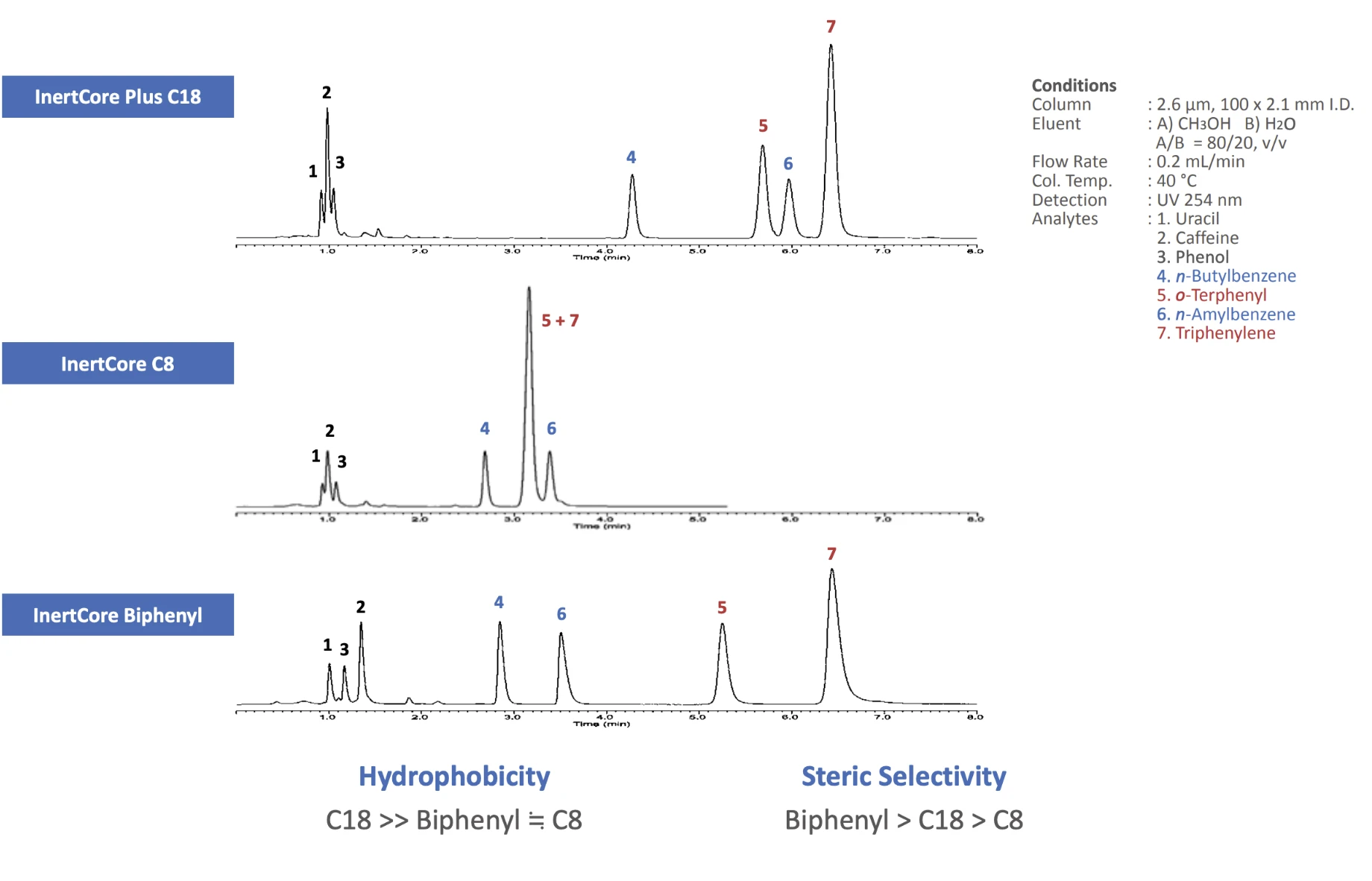
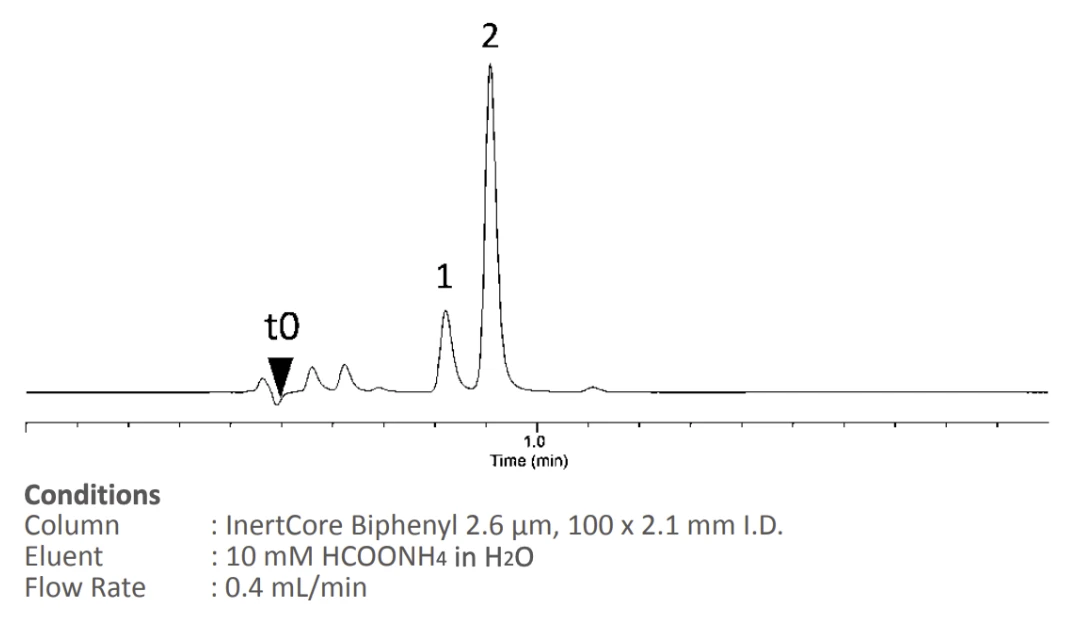
- InertCore Biphenyl Core-shell biphenyl for UHPLC/HPLC with superior π-π selectivity and strong retention of aromatic compounds.
- InertCore C8 Core-shell C8 for UHPLC/HPLC with moderate hydrophobicity, enabling fast, efficient, reproducible separations.
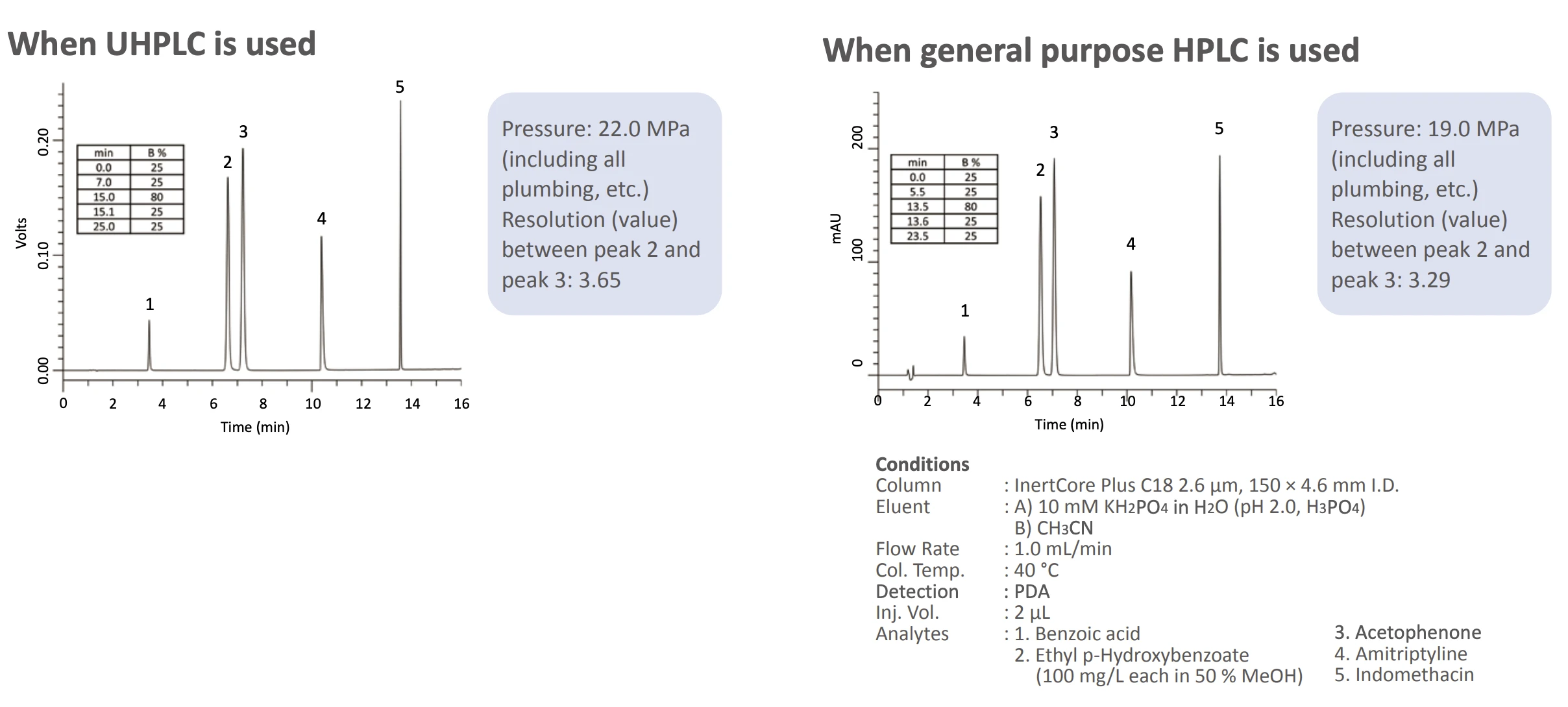
- InertCore Plus C18 Core-shell C18 for UHPLC/HPLC with superior reproducibility, durability, and sharp peaks.
- InertSustain C8 Ultra-inert C8 column for rapid analysis of hydrophobic compounds with symmetric peaks across a wide pH range.
- Inertsil C8 Ultra-pure silica C8 column for rapid analysis of hydrophobic compounds, ideal for legacy methods.
- InertSustainSwift C8 Ultra-inert C8 column for low-polarity analytes, peptides, and oligonucleotides with optimized 200Å pore size.
- Inertsil C8-3 Strong retentivity, very inert, and low back pressure, based on the same silica and bonding as Inertsil ODS-3.
- Inertsil WP 300 Wide-pore C8 column for rapid, high-resolution separation of proteins and peptides with sharper peaks.
- Inertsil C4 Low-retentivity C4 column for rapid analysis of highly hydrophobic compounds like fat-soluble vitamins.
- All C8 & C4 Columns visible-xs
- InertSustain Amide First choice for HILIC mode, offering the strongest retention of polar compounds with superior stability in water-rich conditions.
- Inertsil HILIC Diol-bonded HILIC column for excellent peak shape and strong retention of highly polar basic compounds.
- InertSustain NH2 First choice for sugar analysis, offering superior stability, reproducibility, and compatibility with weakly acidic eluents.
- Inertsil NH2 Aminopropyl column for sugar analysis, highly retentive in normal phase with superior stability and reproducibility.
- ProteoSil HILIC Bioseparation-focused HILIC column, excelling in hydrophilic compound, peptide, glycan, and oligonucleotide analysis.
- All HILIC Columns visible-xs
- InertSustain PFP A pentafluorophenyl-modified column designed for enhanced separation of structurally similar compounds through multiple retention mechanisms, including π-π, dipole, and hydrogen bonding interactions.
- InertSustain Phenyl A directly bonded phenyl group gives the InertSustain Phenyl column unique reversed-phase selectivity, ideal for separating polar compounds and structural isomers via π-π and hydrogen bonding interactions.
- InertSustain Phenylhexyl A phenylhexyl-bonded column that offers complementary selectivity to traditional alkyl-chain columns, providing high inertness, reproducibility, and low back pressure.
Get the Right Column for Your Compound — InstantlyWhat compound are you analyzing? - Sample Preparation
- Close Menu ×
- SPE Cartridges & Columns
- Spin Columns
- Proteomics Products
- InertSep QuEChERS kit
- Cleanup/Separating Bulks
- SPE Manifolds
- ALL Sample Preparation
- InertSep C18 Silica sorbent with high end-capping, ideal for lipid removal & pesticide residue analysis.
- InertSep C18-ENV C18 sorbent with low end-capping, optimized for water analysis & anionic surfactant removal.
- InertSep HLB Versatile SPE column for extracting non-polar to highly polar compounds, with a wide pH range (1-14).
- InertSep C8 Silica sorbent with octyl groups, offering weaker retention than C18 for highly retained compounds.
- InertSep SCX Silica-based SPE column with strong cation exchange and non-polar interactions for enhanced retention.
- InertSep SAX Monofunctional C18 sorbent with medium end-capping, allowing secondary interactions for versatile use.
- All SPE Cartridges & Columns visible-xs
- MonoSpin C18 High-permeability spin column for peptide desalting, drug extraction, and fast biological sample preparation.
- MonoSpin ProA Fast Protein A spin column for high-purity IgG antibody purification with >90% recovery.
- MonoSpin C18-CX Mixed-mode spin column with C18 and cation exchange for enhanced basic drug recovery.
- MonoSpin Phospholipid TiO₂/ZrO₂-coated spin column for efficient phospholipid removal and matrix effect reduction.
- MonoSpin SAX Strong anion exchange spin column for fast extraction of acidic drugs with high recovery.
- MonoSpin TiO TiO₂ spin column for phospholipid removal and organophosphorus pesticide purification.
- All Spin Columns visible-xs
- Exosome Purification
- Desalting
- Digestion
- Fractionation
- Phosphopeptide Enrichment
- Centrifuge Accessories
 InertSep QuEChERS Kit High-purity extraction and cleanup kit for pesticide residue analysis in food and environmental samples.
InertSep QuEChERS Kit High-purity extraction and cleanup kit for pesticide residue analysis in food and environmental samples.
Get the Right Column for Your Compound — InstantlyWhat compound are you analyzing? - GC Columns
- InertCap 1MS General purpose, Hydrocarbons, PCBs, High Volatile solvents, Phenols
- InertCap 1 General purpose, Hydrocarbons, PCBs, High Volatile solvents, Phenols
- InertCap 5MS/Sil General purpose, Halogenated compounds, Phenols, Pesticides, FAME
- InertCap 5MS/NP General purpose, Halogenated compounds, Phenols, Pesticides, FAME
- InertCap 5 General purpose, Halogenated compounds, Phenols, Pesticides, FAME
- InertCap 624MS Residual solvents of Pharmaceuticals, VOCs, Alcohols
- All GC Columns visible-xs
Get the Right Column for Your Compound — InstantlyWhat compound are you analyzing? - Instruments
 LD249 Gas Leak Detector Compact, easy-to-use leak detector with thermal conductivity sensor for fast, accurate gas detection. Replaces the LD239.
LD249 Gas Leak Detector Compact, easy-to-use leak detector with thermal conductivity sensor for fast, accurate gas detection. Replaces the LD239. FM4: Air Sampler for PFAS Low-volume air sampler for PFAS enabling comprehensive analysis of both gas and particle phases in a single sampling using stage-optimized materials.
FM4: Air Sampler for PFAS Low-volume air sampler for PFAS enabling comprehensive analysis of both gas and particle phases in a single sampling using stage-optimized materials. Intelligent Pump UI-32 Series Next-generation dual-plunger HPLC pump with ultra-low pulsation and automated pressure control for flow chemistry.
Intelligent Pump UI-32 Series Next-generation dual-plunger HPLC pump with ultra-low pulsation and automated pressure control for flow chemistry. OralChroma Halitosis Measuring Device High-precision breath analyzer using gas chromatography to quantify VSCs in 4 minutes — fast, reliable, and maintenance-free.
OralChroma Halitosis Measuring Device High-precision breath analyzer using gas chromatography to quantify VSCs in 4 minutes — fast, reliable, and maintenance-free.
 LD249 Gas Leak Detector Latest model replacing LD239, with thermal conductivity detection for helium, hydrogen, and other gases.
LD249 Gas Leak Detector Latest model replacing LD239, with thermal conductivity detection for helium, hydrogen, and other gases. GF1010 Digital Gas Flowmeter Portable, volumetric meter for accurate GC gas flow measurement without gas selection.
GF1010 Digital Gas Flowmeter Portable, volumetric meter for accurate GC gas flow measurement without gas selection.
 Intelligent Pump UI-32 Series Next-generation dual-plunger HPLC pump with ultra-low pulsation and automated pressure control for flow chemistry.
Intelligent Pump UI-32 Series Next-generation dual-plunger HPLC pump with ultra-low pulsation and automated pressure control for flow chemistry. Intelligent Micro Pump MP-32 Series Compact micro pump with ultra-low pulsation and high-pressure stability, ideal for flow chemistry and precision dosing.
Intelligent Micro Pump MP-32 Series Compact micro pump with ultra-low pulsation and high-pressure stability, ideal for flow chemistry and precision dosing. Auto BPR BP-11 Auto Back Pressure Regulator for the UI-22 Series, maintaining stable pressure for consistent flow.
Auto BPR BP-11 Auto Back Pressure Regulator for the UI-22 Series, maintaining stable pressure for consistent flow. PCS Pump SP-32 Series Single plunger pump with real-time pressure control and low-pulsation flow—ideal for precise fluid delivery.
PCS Pump SP-32 Series Single plunger pump with real-time pressure control and low-pulsation flow—ideal for precise fluid delivery.- All HPLC Pumps visible-xs
 Gastorr AG Series Reliable, CPU-controlled degassing system for low-flow applications with independent chamber design.
Gastorr AG Series Reliable, CPU-controlled degassing system for low-flow applications with independent chamber design. Gastorr BG Series High-performance degassing system with real-time vacuum display and independent chamber design.
Gastorr BG Series High-performance degassing system with real-time vacuum display and independent chamber design. Gastorr FG-42 Solvent degassing system optimized for fluorinated solvents with real-time vacuum display.
Gastorr FG-42 Solvent degassing system optimized for fluorinated solvents with real-time vacuum display. Gastorr PG Series High-flow degassing system for fractionating applications with real-time vacuum display.
Gastorr PG Series High-flow degassing system for fractionating applications with real-time vacuum display.- All Degassing Units visible-xs
- Accessories
- Close Menu ×
- HPLC Accesories
- SPE Accessories
- GC Accessories
- HPLC Tubing
- Filters
- HPLC Fittings
- Solvent Bottle Caps and Other Accessories
- Gradient Mixer
- Regulator
- IDEX Accessories
- HPLC Column Hardware and Other Accessories
- Vials
- SPE Vacuum Manifolds
- SPE Gravity Manifolds
- Cleanup/Separating Bulks
- Glass Chromatography Columns
- General SPE Accessories
- Applications & Industries
- Close Menu ×
- Featured
- PFAS Solutions Products and workflows for EPA and ISO-compliant PFAS testing in water, air, and soil.
- Flow Chemistry Solutions Integrated pumps and pressure regulators for continuous, high-temperature flow chemistry reactions.
- Life Science/Bio Products Spin columns and purification tools for antibody capture, protein cleanup, and bioseparation workflows.
- Gas/Air Sampling Equipment Sampling tools for capturing VOCs, aldehydes, and trace gases in environmental and industrial settings.
- Resources
- About
- Contact Us